Objective
Perform CRUD operations on MongoDB database by using Nodejs. We will be using an example of a library database in which we will create, read, update and delete documents for a member in the members collections of the database.
Prerequisite
MongoDB installed in the system and added to environment variables. Can be downloaded from mongodb.com/try/download/community
Nodejs Installed in the system, can be installed from: nodejs.org/en/download
VSCode or any other text editor.
Introduction of Mongo Shell commands is recommended but not mandatory. Can be refered from: asimjunaidcodes.hashnode.dev/mongodb-crud-o..
Getting Started
Starting MongoDB
To start MongoDB run the command in Command Prompt in Windows, Bash in Linux/Unix or Terminal in MacOS.
mongod
Incase case of error, check if the MongoDB directory location is added to your environment variables.
Setup the Coding Environment
Open VS Code terminal or from any other terminal (cmd/bash) execute the commands in the directory where you are building your project and execute the following commands:
- Initialse npm, which is the nodejs package manager:
npm init -y
- Install the mongodb node module:
npm i mongodb
This is the official module for nodejs by mongodb and we will be using this to work with mongodb database.
Connect to database
Create a file index.js, this is where we write our code. We will first import the mongodb module we have just installed. We do this by following code:
const mongodb = require('mongodb');
The MongoClient will help us to create connection and ObjectId is used to uniquely identify a document form its _id field.
const mongodb = require('mongodb')
const MongoClient = mongodb.MongoClient
const ObjectId = mongodb.ObjectId
let databaseName = 'library'
Here for simplicity purpose we have done it separately. However a simpler approach would be:
const {MongoClient, ObjectID} = require('mongodb');
To establish connection on the localhost(127.0.0.1) we use the MongoClient.connect() method.
MongoClient.connect('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017', (error, client)=>{
if(error){
throw Error('Could not connedted to database. \nError:' + error.message);
}
console.log('Connected to database.')
const db = client.db(databaseName);
})
By default MongoDB uses 27017 as its default port number. The second argument is a callback function with arguments:
error: This gives the error message when an error occurs, otherwise is undefined or null.result: The second argument (here we have called itclient) will contain the initialised database object and will be used by us to execute operations.
On succesfully runnning the file you will get a message on your console as "Connected to database.".
Create Document
Insert One Document
Suppose we want to insert a document for a member with: {"name": "Asim", "joining_year" : 2020} in the collection named 'members'. To insert this document we use following code inside the callback funtion of MongoClient.connect():
MongoClient.connect('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017', (error, client)=>{
if(error){
throw Error('Could not connedted to database. \nError:' + error.message);
}
console.log('Connected to database.')
const db = client.db(databaseName);
// Insert Single document
var item = {
"name": "Asim",
"joining_year" : 2020
}
let db = client.db();
db.collection('members').insertOne(item,
(error, result) => {
if(error){
throw Error('An error occured.');
}
console.log('Data inserted !')
console.log(result);
}
);
})
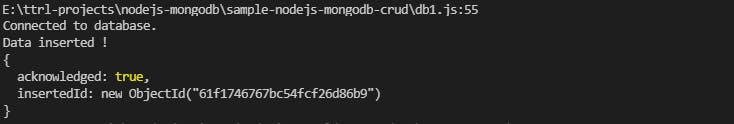
The callback funtion has two arguments similar to the mentioned above. result returns the inserted data's ObjectId() and acknowledgement when execution is successful.
Insert multiple Documents
To inset multiple documents we use insertMany(). The first argument here will be set of items (which are key value pairs).
var items = [
{
"name": "Asim",
"joining_year" : 2020
},
{
"name" : "Fahad",
"joining_year" : 2020
}
]
db.collection('members').insertMany(items,
(error, result) => {
if(error){
throw Error('An error occured.');
}
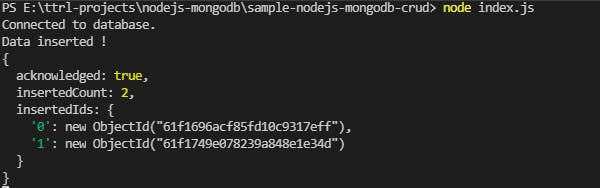
console.log('Data inserted !')
console.log(result);
}
);
Read Document
Query One Document
To read a single document from the members collection, findOne() is used. You can pass a filter in case you want to query a specific data. Passing an empty data will return all the documents in the collection.
MongoClient.connect('mongodb://127.0.0.1:27017', (error, client)=>{
if(error){
throw Error('Could not connedted to database. \nError:' + error.message);
}
console.log('Connected to database.')
const db = client.db(databaseName);
// Read Single document
var filter = {
"name": "Asim"
}
db.collection('members').findOne(filter,
(error, result)=>{
if(error){
throw Error('An error occured');
}
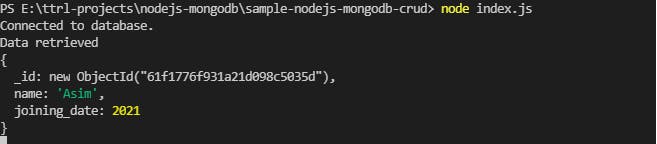
console.log('Data retrieved');
console.log(result);
}
);
})
Query multiple Documents
To query multiple documents we use find(). The first argument here too will a filter(which are key value pairs).
// Read Multiple documents
var filter = {
"name" : "Asim"
}
db.collection('members').find(filter).toArray(
(error, result)=>{
if(error){
throw Error('An error occured');
}
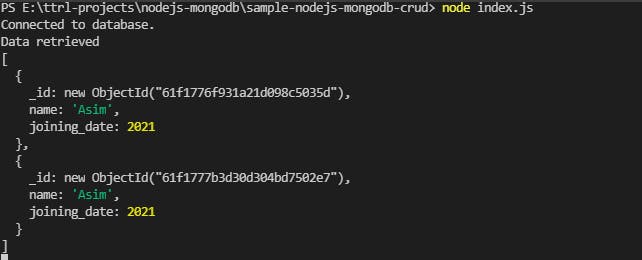
console.log('Data retrieved');
console.log(result);
}
);
A thing to notice here is that both have the same name but different _ids. These are ObjectId()s that can be used to uniquely identify document. We will be using them to update documents.
Update Documents
Update One Document
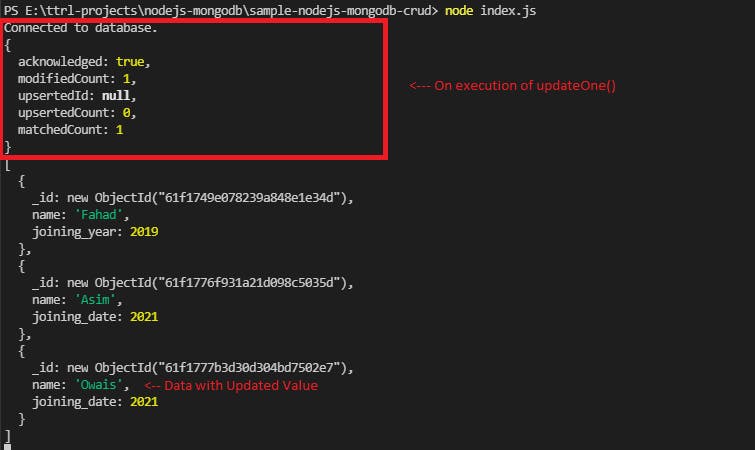
To update a document from the members collection, updateOne() is used. Here in filter, we have used ObjectId() to identify a single document.
// Update one document
var filter = {
"_id": ObjectId("61f1696acf85fd10c9317eff")
}
var updatedValue = {
"name" : "Owais"
}
const updatedPromise = db.collection('members').updateOne(filter,
{
$set: updatedValue
}
);
updatedPromise
.then((result)=> {console.log(result.ops);}) // Prints the updated value if succesfull
.catch((error) => {throw Error('There occured an error');}); // Execution Failed
// retrieve all the documents
db.collection('members').find({}).toArray((error, result)=>{
console.log(result)
})
Update multiple Documents
To update multiple documents we use updateMany().
// Update Multiple documents
var filter = {
"joining_year" : 2020
}
var updatedValue = {
"joining_year" : 2019
}
const updatedPromise = db.collection('members').updateMany(filter,
{
$set: updatedValue
}
);
updatedPromise
.then((result)=> {console.log(result);}) // Prints the updated value if succesfull
.catch((error) => {throw Error('There occured an error');}); // Execution Failed
Delete Documents
Delete One Document
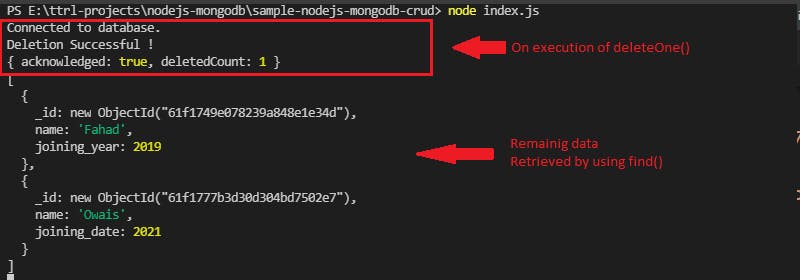
To delete a document from the members collection, deleteOne() is used.
var filter = {
"name" : "Asim"
}
db.collection('members').deleteOne(filter)
.then((result)=>{
console.log('Deletion Successful !');
console.log(result);
})
.catch((error) => {
throw Error('There occured an error');
});
// retrieve all the documents
db.collection('members').find({}).toArray((error, result)=>{
console.log(result)
})
Delete multiple Documents
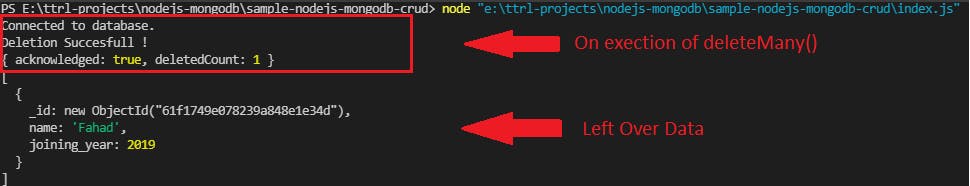
To update multiple documents we use updateMany().
// Update Multiple documents
var filter = {
"joining_date" : 2021
}
db.collection('members').deleteMany(filter)
// retrieve all the documents
db.collection('members').find({}).toArray((error, result)=>{
console.log(result)
})
Conclusion
- In the above blog we gave an example of a library database where we add, remove, update and delete member details in the members collections.
- The operations we performed were:
- Insert document
- Insert single document with:
db.collection(collectionName).insertOne(item) - Insert multiple documents with:
db.collection(collectionName).insertMany(item)
- Insert single document with:
- Read document
- Query single document with:
db.collection(collectionName).findOne(filter) - Query multiple documents with:
db.collection(collectionName).find(filter)
- Query single document with:
- Update
- Update single document with:
db.collection(collectionName).updateOne(filter, $set: updateValue) - Update multiplt document with:
db.collection(collectionName).updateOne(filter, $set: updateValue)
- Update single document with:
- Delete
- Delete single document with:
db.collection(collectionName).deleteOne(filter) - Delete multiple documents with:
db.collection(collectionName).deleteMany(filter)
- Delete single document with:
- Insert document

