Photo by Nick Morrison on Unsplash
Diary Application in JavaScript(nodejs) with File Management, Date class and Yargs
Objective
We will be creating a node application with file management system using the fs module, object of Date() class and yargs module. We will be creating a diary. The user will only enter the content. The program will take care of of storing with the specified date and display when asked with the diary entry format.
Prerequisite
- Nodejs installed in the computer. Can be installed from: nodejs.org/en/download.
- VS Code or any other text editor.
Getting Started
Setting up the environment
Here I will be using VS Code, you can use any code editor of your choice. Create and open a project folder create a file and create these files:
- write_diary.txt - The user will write the diary content in this text file.
- display_diary.txt - The required diary content will be displayed in this text file.
- diary.txt - All the diary data will be store here in
jsonformat. - index.js - This will consist of all the code.
File can be executed by executing the following command in the terminal:
node index.js
Getting Current Date
When a user creates a diary, the date of the diary entry will be handled by us. We will be doing this with an object of Date(). We can retrieve:
- Day by
Date().getDay() - Date by
Date().getDate() - Month by
Date().getMonth() - Year by
Date().getYear() - Hour by
Date().getHour() - Minute by
Date().getMinute()
To this we we will be creating a getTimeStamp() function.
var timeStamp = ()=>{
var dateInstance = new Date() // object of Date()
var date1 = dateInstance.getDate()
var month= dateInstance.getMonth() + 1
var year = dateInstance.getFullYear()
var amOrPm = 'AM' // By default it will be 'AM'
var day
switch(dateInstance.getDay()){ // getDay() returns an integer value, 0 for Sunday, 1 for Monday etc
case 0: day = 'Sunday';
break;
case 1: day = 'Monday';
break;
case 2: day = 'Tuesday';
break;
case 3: day = 'Wednesday';
break;
case 4: day = 'Thursday';
break;
case 5: day = 'Friday';
break;
case 6: day = 'Satuday';
break;
}
var date = date1 + '/' + month + '/' + year; // Date in format DD / MM / YYYY
var hour = dateInstance.getHours()
if (hour > 12){
hour = hour%12; // Cuz we will be displaying in 12 hour format
amOrPm = 'PM'
}
var timeStamp = hour + ' : ' + dateInstance.getMinutes() + ' ' + amOrPm;
return {day, date, timeStamp}
}
The above function would give me a value:
{ day: 'Satuday', date: '29 / 1 / 2022', timeStamp: '9 : 47 PM' }
As this was my systems timings while executing the function. You would get the current time for your system.
Write Diary Function
Read data from file
The write_diary() function will take the diary content from the write_diary.txt and store it in diary.txt . To read the contents of a file we use the fs module which can be imported by:
const fs = require('fs')
Initialse a write_diary() function. In this we will read the contents of the write_diary.txt. Contents of the file can be read by using the readFileSync() method from the fs module. This method returs Buffer data. We will convert it into a string by .toString() method.
var writeDiary = ()=>{
var content = fs.readFileSync('write_diary.txt').toString()
console.log(content) // To print the content in the console.
}
Now will first retrieve the current time by calling the getTimeStamp() function and store it in a date variable.
var time = timeStamp()
We will create an object data in which we will store te time and content retrived.
Write/Append data in file
To store a javaScript object into a text file so that we can later retrieve it as JSON. We need to stringfy() the object which means will convert it into a string and the write it into the file. To write into the file we use the writeFileSync() method of the fs module. Since there will be older data to its better to use the appendFileSync() method which will actually just append the file instead of overwriting it.
fs.appendFileSync('diary.txt', JSONdata);
Our writeDiary() would look like this:
var writeDiary = ()=>{
var content = fs.readFileSync('write_diary.txt').toString()
// console.log(content)
if(content.length == 0){
console.log('No note added')
return;
}
var time = timeStamp() // Get current time stamp
// console.log(time)
var data = {
time: time,
content: content
} // JSON structure with javaScript Objects
var JSONdata = JSON.stringify(data)
// console.log(JSONdata)
var earlierData = fs.readFileSync('diary.txt').toString() // Reading data from diary
// Appending data by using the writeFileSync() method
// if(earlierData.length > 0){
// earlierData = earlierData + ',' // Adding comma if not first document of the json
// }
// fs.writeFileSync('diary.txt', earlierData + JSONdata); // Entering data in diary
if(earlierData.length > 0){
JSONdata = ',' + JSONdata // Adding comma if not first document of the json
}
fs.appendFileSync('diary.txt', JSONdata);
// Overwriting the write_diary.txt with empty string/text
fs.writeFileSync('write_diary.txt', '');
}
Test the current functionality
To test the current functionality:
- Write and save in write_diary.txt and save.
- Call the function
writeDiary()function at the end. - Run the
index.jsfile by executing the command:
node index.js
A JSON styled text would be written and stored in the diary.txt file.
Read Diary Function
The user will specify the date of which he wants to read the content. This fucntion will retrieve that specified content from the diary.txt file and write it in the display_diary.txt file in the diary entry format which will include the time stamp of when the diary was entered.
Retrieve data and parse String to JSON
First, read the data from the diary.txt. And the parse it into JSON by using the JSON.parse(). We will add square brackets [ ] before the string to make it into and array of objects when parsed into JSON.
var readDiary = (requiredDate)=>{
// requiredDate is the specified date for which data is retrieved
var content = fs.readFileSync('diary.txt').toString() // Buffer data TO String
var contentJSON = JSON.parse('[' + content + ']') // String to JavaScript Object
// console.log(contentJSON)
}
We will initialise a list diaries in which we will add all the diary content that match the requiredDate.
var diaries = []
for(var i in contentJSON){
var date = contentJSON[i].time.date
if(date==requiredDate){
diaries.push(contentJSON[i])
// console.log(contentJSON[i])
}
}
Now diaries will contain the required content from the contentJSON array. This content will be formatted and then written in the display_diary.txt file in diary entry format with the time stamp.
var requiredDiaryContents = []
content = '';
for(var i in diaries){
var diary = diaries[i];
var time = diary.time;
var diaryTime = time.date + '\n' + time.day + ', ' + time.timeStamp + '\n\n';
var content = content + diaryTime + diary.content + '\n\n\n\n';
requiredDiaryContents.push(content)
// DD / MM / YYYY
// SUNDAY, 10 : 25 PM
// CONTENT
// CONTENT
}
if(content.length == 0){
console.log('Date data not present or invalid')
}
fs.writeFileSync('display_diary.txt', content);
Complete readDiary() function:
var readDiary = (requiredDate)=>{
var content = fs.readFileSync('diary.txt').toString() // Buffer data TO String
var contentJSON = JSON.parse('[' + content + ']') // String to JavaScript Object
// console.log(contentJSON)
var diaries = []
for(var i in contentJSON){
var date = contentJSON[i].time.date
if(date==requiredDate){
diaries.push(contentJSON[i])
// console.log(contentJSON[i])
}
}
var requiredDiaryContents = []
content = '';
for(var i in diaries){
var diary = diaries[i];
var time = diary.time;
var diaryTime = time.date + '\n' + time.day + ', ' + time.timeStamp + '\n\n';
var content = content + diaryTime + diary.content + '\n\n\n\n';
requiredDiaryContents.push(content)
// DD / MM / YYYY
// SUNDAY, 10 : 25 PM
// CONTENT
// CONTENT
}
if(content.length == 0){
console.log('Date data not present or invalid')
}
fs.writeFileSync('display_diary.txt', content);
}
You now run the appliation again and call the readDiary() function by specifying one of the dates from the stored data.
Input from Command Line Arguments
The above appliation will still work, however in order to make the user interactivity much better and we will use the command line arguments.
Installing Yargs Module
We will be using the yargs module to accept these command line arguments. For this we will first need to initialse npm which is the Node Package Manager. This can be done by executing the following command in the terminal:
npm init
Now install the yargs module:
npm i yargs
Yargs Commands
The commands()method will help us to specify the command from the command line argument. We can do this by:
yargs.command({
command: 'read',
describe: 'Read diary from the specified date',
builder: {
date: {
type: 'string'
}
},
handler: (argv)=>{
readDiary(argv.date)
console.log('Read diary from the file display_diary.txt. ')
}
})
yargs.parse() // Should be used after all the yargs statements
The command() accepts a javaScript object.
- The
commandobject specifies the command, here either we want to read or write. describegives a description of what the command will do. This will be shown whennode index.js --helpis executed in termninal.- The
builderobject specifies the arguments that the user will give. - The
handleris executed on executing the specific command.
Here we specified that when the read command is executed we call the readDiary() function. Rerieve date argument specified in the builder by argv.date and pass it into the function. To execute the read command, execute the following in the terminal.
node index.js read --date='29/1/2022'
Similaly we can do it for the write command. Try to do this yourself, if you find any troble you already have the code at the end.
yargs.command({
command: 'write',
describe: 'Read diary from the specified date',
handler: (argv)=>{
writeDiary()
console.log('Diary added')
}
})
yargs.parse()
Write your content in the write_diary.txt and execute by:
node index.js write
Screenshots
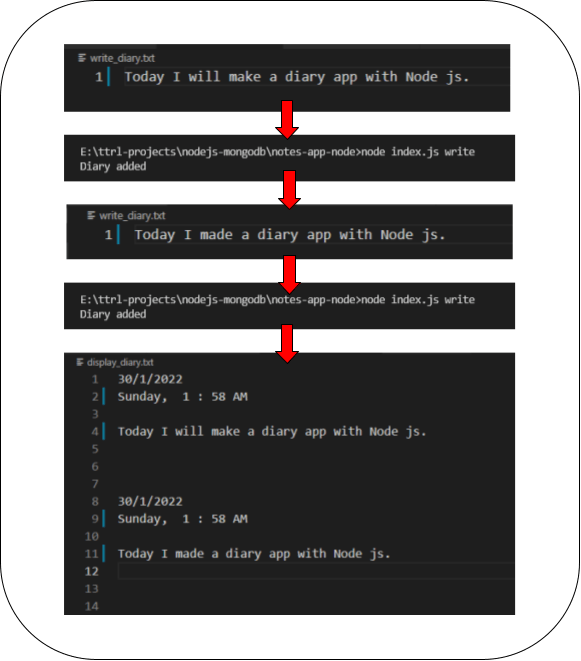
Conclusion:
Object of
Dateis used to get the current date.- Day by
Date().getDay() - Date by
Date().getDate() - Month by
Date().getMonth() - Year by
Date().getYear() - Hour by
Date().getHour() - Minute by
Date().getMinute()
- Day by
Synchronous File Mangement can be done by using the
fsmodule.- To read a file synchronously
fs.readFileSync('filename'). - To write a file synchronously
fs.writeFileSync('filename', content) - To write a file synchronously
fs.appendFileSync('filename', content)
- To read a file synchronously
- Reading a file returns Buffer data. This data can be converted into a string using the
bufferData.toString()function. - A javaScript object can be converted into string using,
Json.stringify(object). - A JSON formatted script can be converted into a json object using the
JSON.parse(string). - Yargs can be used to accept command line arguments.
- A yargs command is made using
yargs.command(object).- The
commandobject specifies the command, here either we want to read or write. describegives a description of what the command will do. This will be shown whennode index.js --helpis executed in termninal.- The
builderobject specifies the arguments that the user will give. - The
handleris executed on executing the specific command.
- The
