Objective
Perform CRUD operations on MySQL database with Nodejs. Here we will create a database "library" and perform CRUD operations on it by inserting data about books in a table "books".
Prerequisite
- MySQL installed in the system. Can be downloaded from: dev.mysql.com/downloads/installer
- Nodejs installed in the computer. Can be installed from: nodejs.org/en/download.
- VS Code or any other text editor.
Getting Started
Install required package
We will be installing the mysql2 module. However mysql is also a module which helps us in achieving the same goal, but here we will be using the mysql2 since mysql has some complications with MySQL version >= 8.x. You can still use the mysql module if it works for you since it also contain all similar methods. Open VS Code or any other editor and create a folder of your choice. Initialize npm by executing the following command in the VS Code terminal of the same directory and execute the command:
npm init -y
To install the mysql2 module:
npm install mysql2
Create a new file index.js. This is where we will add all our code.
Create MySQL Database
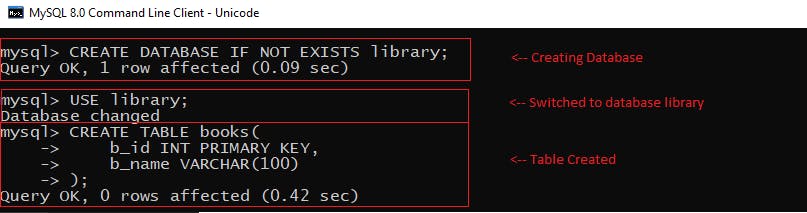
Open MySQL CLI or any other MySQL client like MySQL Workbench and execute the following commands to create a database and its tables:
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS library;
USE library;
CREATE TABLE books(
b_id INT PRIMARY KEY,
b_name VARCHAR(100)
);
This will create a database library. In this library we created a table books in which we will perform CRUD operations.
Connect to the Database
Import the mysql2 module
var mysql = require('mysql2');
We can now connect to the database by using mysql.createConnection()
var mysql = require('mysql2');
var connection = mysql.createConnection({
host: 'localhost',
user: 'root',
password: 'root',
database: 'library_management_system1'
});
Username and password in my system is 'root'. However you may enter according to your configuration. In case there's no password, you can skip the password field.
Performing Operations
Now we will create functions which will help us to execute our query. To perform the queries we use the queries() method.
Inserting Record
We will insert a book record in the library database. Our function will accept book name and a book id to insert it in the table.
var insertBook = (sqlparam)=>{
}
sqlparam will be a list of parameters. Now suppose we want to insert a books with b_name = "Wings of Fire" with b_id = 1. The general SQL query would be INSERT INTO books VALUES(1, "Wings of Fire"). So sqlparam would be [1, "Wings of Fire"]. To insert the data:
var insertBook = (sqlparam)=>{
var sqlQuery = 'INSERT INTO BOOKS VALUES(?, ?)';
connection.query(sqlQuery, sqlparam, (error, results, fields)=>{
if(error){
console.log(e);
}
console.log(results);
});
}
In the sqlQuery we have used "?" in place of parameters. The connection.query() takes first argument as the query and the second is the list of parameters. The third is the callback function with 3 arguments which gets executed after the insertion query is executed in the database. The 3 arguments are:
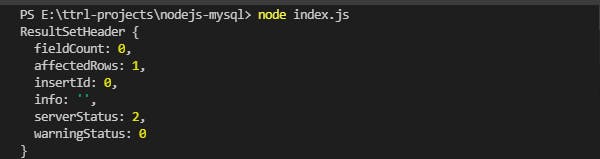
error: This contains the error message when there is a faliure in the execution else is undefined or null.results: This contains the result when the execution is successfully completed.fields: Contains the extra meta data about the result.
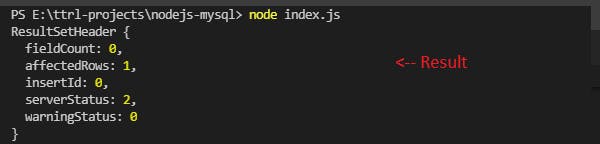
Let's now insert data into the database by calling the insertBook function:
sqlParam = [1, "Wings of fire"]; //Parameters
insertBooks(sqlParam); // Calling the insetBooks() function
Query/Read Record
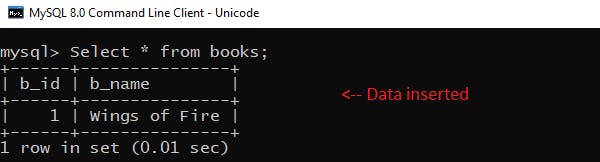
Now we will create a function to read the data inserted. We are using b_id parameter to identify :
var getBooks = (sqlparam)=>{
var sql = 'SELECT * FROM BOOKS WHERE b_id = ?';
connection.query(sql, sqlparam, (error, results, fields)=>{
if(error){
console.log(e);
}
console.log(results)
});
}
We call the getBooks() function below:
var sqlParam = [1]; // b_id of the record we recently inserted
getBooks(sqlParam);
The results give an array of records matching the criteria. In our case since there is only one record matching it, our array consists of just one record.

Update Record
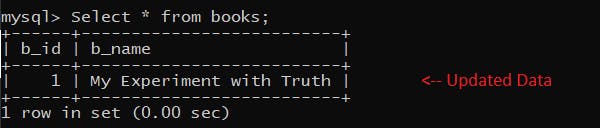
Now we will update the name of the books to "My Experiments with Truth".
var updateBook = (sqlparam)=>{
var sqlQuery = 'UPDATE BOOKS SET b_name = ? where b_id = ?';
// SQL Query for Modification
connection.query(sqlQuery, sqlparam, (e, results, fields)=>{
if(e){
console.log(e);
}
console.log(results)
});
}
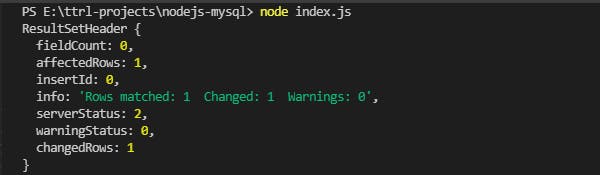
Call the function:
var sqlParam = ["My Experiment with Truth", 1]
// First Parameter is the new book name to be updated and
// second is the b_id for identification of particular record.
updateBook(sqlParam);
Delete Data
We will be deleting the data again by using the b_id to uniquely identify the record.
var deleteBook = (sqlparam)=>{
var sqlQuery = 'DELETE FROM BOOKS WHERE b_id = ?';
connection.query(sqlQuery, sqlparam, (e, results, fields)=>{
if(e){
console.log(e);
}
console.log(results)
});
}
Call the function:
var sqlParam = [1] // b_id to uniquely identify the record
deleteBook(sqlParam);

Conclusion
- In the blog we used the example of a database library where we worked on the books table.
- The operations that can be performed by
connection.query(sqlQuery, sqlparam, callback). - The SQL Query consists of "?" in place of parameters.
- The parameters are passed as a list.
- On succesfull execution the
resultscontains the result andfieldits meta deta. - In case of error,
errorcontains the error message and can be used to throw an error else it is undefined or null.

